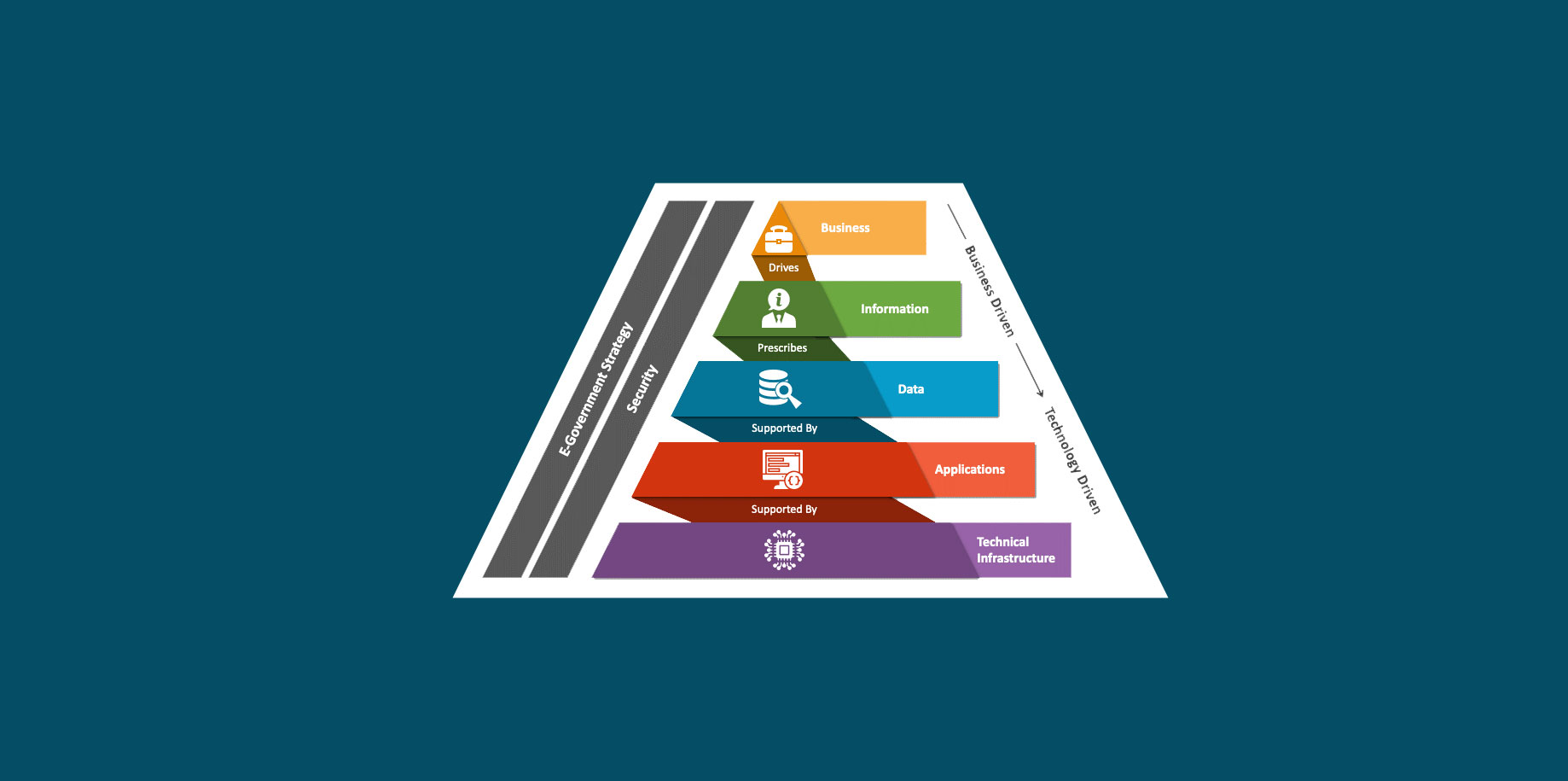
An enterprise data architecture framework (EDAF) is
a structured approach to managing and organizing
data within an organization. It encompasses the
entire data lifecycle, from collection and storage to
processing and analysis. Data governance plays a foundational role in EDAF, setting policies, roles, and responsibilities to maintain data integrity, consistency, and compliance with legal and industry standards. It ensures that data is managed ethically and transparently, establishing a reliable data environment that supports regulatory requirements.
Data modeling: is another essential component, visually representing data structures, relationships, and flows across various systems. This allows for a clear understanding of how data entities interact and aids in designing scalable, organized data solutions. Metadata management, meanwhile, adds context to data by documenting its source, use, and attributes. By maintaining high-quality metadata, organizations can make data more discoverable, traceable, and actionable.
Data governance: plays a foundational role in EDAF, setting policies, roles, and responsibilities to maintain data integrity, consistency, and compliance with legal and industry standards. It ensures that data is managed ethically and transparently, establishing a reliable data environment that supports regulatory requirements. Data modeling is another essential component, visually representing data structures, relationships, and flows across various systems. This allows for a clear understanding of how data entities interact and aids in designing scalable, organized data solutions. Metadata management, meanwhile, adds context to data by documenting its source, use, and attributes. By maintaining high-quality metadata, organizations can make data more discoverable, traceable, and actionable.
Data integration within EDAF: combines data from multiple sources, creating a unified and accessible view of information. This includes the use of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes, which enable efficient data migration, cleansing, and transformation to support analytics and operational functions. Data security is paramount in EDAF, covering encryption, access controls, and audit trails to safeguard sensitive information. Compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is integral to data security, ensuring data is handled in a way that respects privacy and legal obligations. EDAF’s approach to data lifecycle management ensures that data remains relevant and compliant. By systematically archiving or disposing of obsolete data, the framework supports organizational efficiency and security.
The benefits of EDAF: implementation are far-reaching, encompassing improvements in data quality, operational efficiency, and overall decision-making capabilities. By eliminating data silos and standardizing data practices, organizations can ensure that data is reliable, accessible, and consistent across departments. Data quality management within EDAF focuses on maintaining high standards of accuracy, completeness, and reliability. This involves data profiling, validation, and cleansing, ensuring data remains fit for use across various functions.
A successful EDAF: aligns closely with the organization’s overall data strategy, linking data practices directly to business objectives. This alignment ensures data initiatives are not siloed but rather contribute to the broader mission of using data as a strategic resource. Data stewardship plays a crucial role, assigning individuals responsibility for data quality and policy adherence within specific domains. Data stewards help enforce governance standards and support best practices as defined in the EDAF. Data cataloging adds another layer, making it easier for users to locate and leverage data. An organized, searchable data catalog enhances governance by giving stakeholders clear visibility into available data assets.
Data lineage is a powerful aspect of EDAF, mapping data from its point of origin through its various transformations and uses. This transparency supports compliance, troubleshooting, and auditing efforts, enabling organizations to monitor data flows and transformations. Master Data Management (MDM) in EDAF ensures that core data entities, like customer or product information, remain consistent and reliable across the organization. MDM reduces redundancy and establishes a single source of truth, supporting improved data integration and reporting.
EDAF follows key principles: such as modularity, scalability, and interoperability, ensuring that the data architecture can adapt to changing needs, accommodate growth, and integrate with other systems. ETL and ELT processes are central to transforming raw data into useful information for analysis and reporting, with ETL commonly used in data warehousing and ELT in big data environments where large datasets are stored before being analyzed. EDAF also adapts to the demands of big data, allowing organizations to process and analyze high-volume, high-velocity data from various sources.
Cloud data architecture under EDAF: offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility. Cloud-based architectures support remote access, real-time processing, and disaster recovery, meeting the needs of modern enterprises. Data warehousing within EDAF consolidates data from various sources, supporting comprehensive analysis and reporting. A data warehouse offers a historical view that enables organizations to identify trends and make data-driven decisions. Data lakes and data lakehouses complement data warehouses by providing flexible storage for unstructured and semi-structured data, while lakehouses blend the benefits of both data lakes and warehouses to support varied data types.
Data virtualization offers: another solution, providing real-time access to data across disparate sources without the need for physical data movement. This approach enables faster insights and reduces the complexity and cost of traditional data integration methods, enhancing EDAF’s agility.